PCB and PWB are often heard in the realm of electronics manufacturing. While frequently used interchangeably, a subtle but important technical and historical distinction exists between them.
The Historical Origin of PCB and PWB
The term Printed Wiring Board (PWB) is actually the older name. It was coined to describe the core function of the board: a non-conductive substrate with etched copper pathways that form the “wires” of a circuit. In many regions, particularly Japan, print wiring board remains the standard term to refer specifically to the bare, unpopulated board. Printed Circuit Board, emerged later as a more comprehensive term that describes the final, assembled product.
The Manufacturing Journey from PWB to PCB
This evolution in terminology perfectly describes the manufacturing process. It begins with the fabrication of the bare PWB, which is essentially the foundational platform. The journey is completed when electronic components are soldered onto this platform, transforming it into a fully functional PCB. Therefore, every assembled PCB starts its life as a PWB.
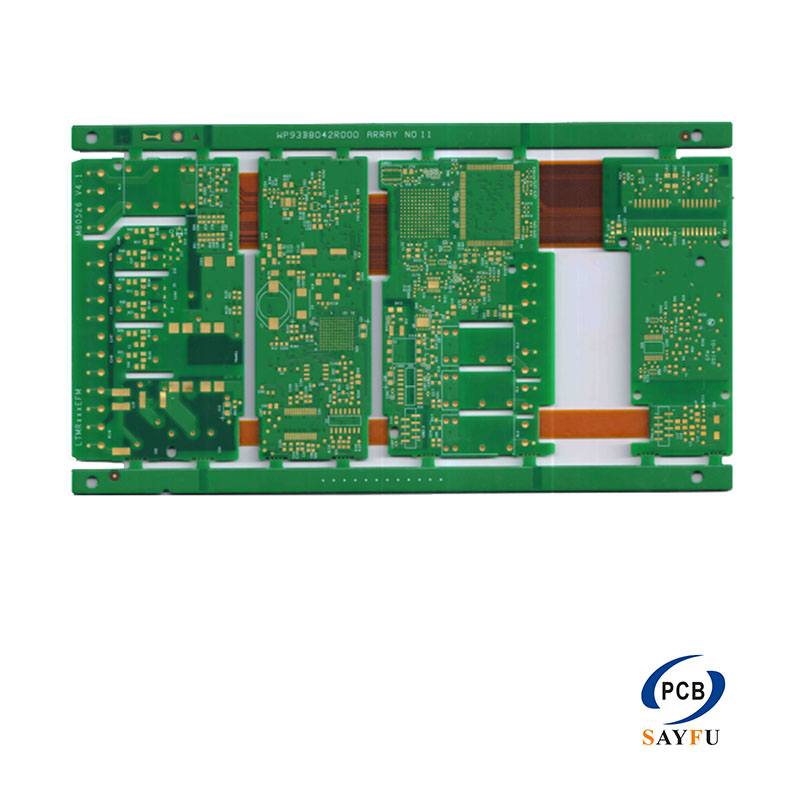
Print circuit board in Global Terminology
The preference for PCB and PWB often depends on geographic location and industry tradition. While PWB is entrenched in Japanese technical jargon, PCB has become the globally dominant and universally understood term. In most international contexts, PCB serves as the umbrella term for both the bare board and the assembled unit, though the precise distinction between Print circuit board and Print Wring board remains important for engineers and manufacturers.
The Functional Role of PCB
Despite the naming nuance, the functional role of PCB and PWB technology is undeniable. It provides the critical physical structure and electrical connections for components. From smartphones to medical devices, the innovation encapsulated in prinit circuit board design is the invisible backbone of the modern electronic age, enabling the miniaturization and complexity of the devices we rely on daily.
Understanding the difference between print circuits and print wrings offers a deeper insight into the precise language and intricate processes of electronic engineering.