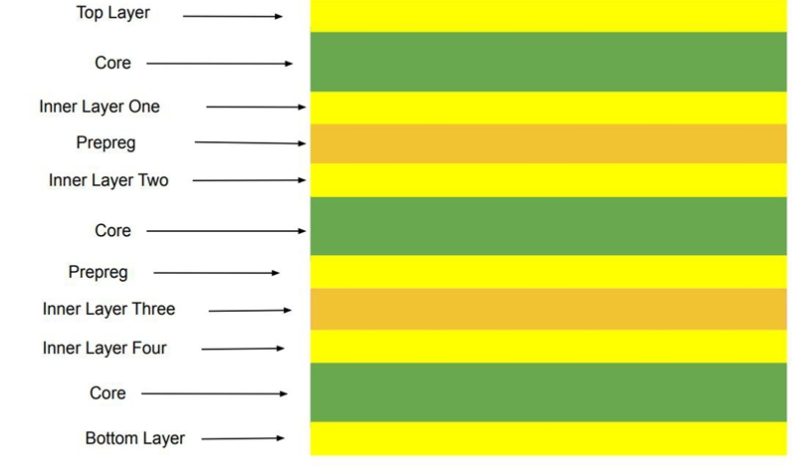
Multilayer PCB: Prepreg, Core, and Copper Foil form the backbone of modern electronics. Their complex structure relies on three essential materials. These elements are laminated together under heat and pressure. Therefore, they create a robust and integrated single board.
1.The Core: Providing Rigidity and Structure
The core is a fundamental building block. It consists of a rigid substrate laminated with copper foil. This component provides the PCB‘s mechanical strength and stability. Furthermore, it serves as the central insulating layer between conductive layers.
2.Prepreg: The Bonding Agent of Prepreg Core and Copper Foil
Prepreg is a pre-impregnated fibrous material, and it is partially cured. This “B-stage” resin flows and cures under heat. Consequently, it permanently bonds cores and foils into a solid composite. It also acts as a critical insulating layer.
3.Copper Foil: The Conductive Pathways
Copper foil creates the circuit’s conductive pathways. It is laminated onto the core and also placed between prepreg layers. After lamination, the foil is etched. Thus, it forms the intricate traces, planes, and pads for components.
4.Conclusion: A Synergistic Fusion
These three elements work in perfect synergy. The core provides structural integrity, while the prepreg binds everything together. Meanwhile, the copper foil enables electrical functionality. Ultimately, their combination allows for the powerful, miniaturized devices we use today.
5.Manufacturing Process and Quality Control
The manufacturing process begins with careful material selection. Next, layers are stacked in a precise sequence. This stack undergoes thermal lamination for bonding. Afterwards, drilled holes connect different conductive layers. Finally, these holes are plated to ensure conductivity.
6.Applications and Future Trends for Prepreg Core and Copper Foil
Multilayer PCBs enable advanced computing and 5G communication. They are also crucial for automotive electronics and medical devices. Furthermore, they support the development of flexible and high-frequency circuits. Emerging technologies continue to push the requirements for these materials. Consequently, manufacturers are developing newer, more advanced material combinations.
