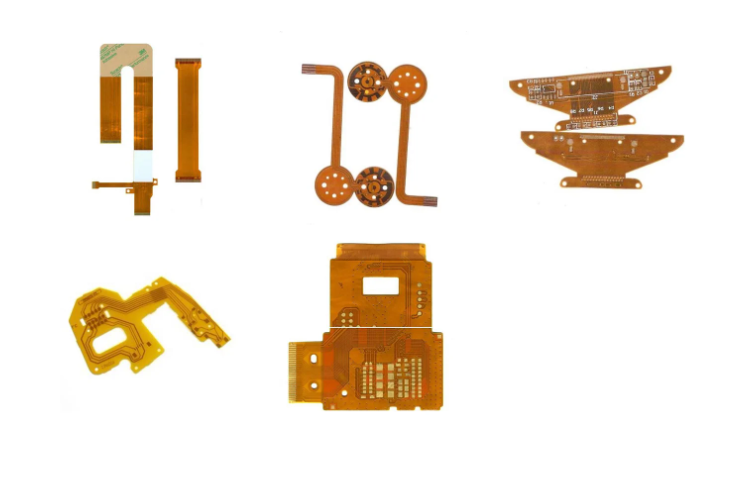
Flexible Printed Circuits (FPC) are flexible circuits built on polyimide or polyester film substrates. They use advantages like flexibility, thinness, and impact resistance to bypass spatial limits of rigid circuits, and are categorized into single-sided, multi-layer boards, etc. Widely used in consumer electronics, automotive, and aerospace.
The FPC industry is currently accelerating its development toward higher circuit density, thinner substrate thickness, and better reliability, and it is continuously releasing its market potential in emerging fields like flexible displays and IoT devices.
Definition and Characteristics of Flexible Printed Circuits
A Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC) is a printed circuit with high flexibility, using polyimide or polyester film as its substrate. Its core characteristics include the ability to bend, fold, and wind freely, enabling adaptation to complex installation spaces. It also features light weight, thin thickness, and high resistance to vibration and impact, breaking through the spatial layout limitations of traditional rigid printed circuits.
Structure and Classification of FPCs
Structurally, FPCs mainly consist of a substrate, a conductive layer (usually electrolytic copper foil), an adhesive, and a protective layer. Some high-end products also include a shielding layer to enhance electromagnetic compatibility (EMC).
- Classification by structure: Single-sided boards, double-sided boards, multi-layer boards, and rigid-flex combined boards.
- Classification by application: Ordinary flexible boards, high-frequency flexible boards, rigid-flex combined boards, etc. Different types meet different performance requirements.
Development and Applications of Flexible Printed Circuits
Currently, FPCs are developing toward higher density, thinner profiles, and multi-layered structures. With the rise of technologies such as 5G, flexible displays, and smart wearables, their application fields continue to expand.
- Consumer electronics: Widely used in flexible cables for foldable screens of smartphones and motherboards of smartwatches.
- Automotive electronics: Suitable for flexible connections in automotive radar and central control systems.
- Aerospace: Utilized in satellite communication equipment due to its lightweight advantage.