Assemble PCB Board is a core process in electronics manufacturing. It connects abstract designs with physical devices. Precise assembly enhances product reliability. Conversely, errors may lead to functional failure. Thus mastering correct methodology is crucial. This is an essential skill for every engineer.
1.Preparation and Component Check Assemble PCB Board
First, gather all necessary tools and materials. These include the PCB, components, and a soldering iron. Always check the component list carefully. Ensure all parts match your design specifications. Next, inspect the PCB for any damage. Look for broken traces or pads. Organize components by their values and types. This prevents confusion during assembly. Finally, prepare your workspace. Good lighting is essential for clear vision.
1.Soldering Components in Order Assemble PCB Board
Start by soldering the shortest components first. This typically includes resistors and diodes. Then, proceed to taller parts like capacitors. Always apply solder to the fixed pad first. Heat the pad and the component lead simultaneously. Next, carefully feed the solder onto the joint. Ensure the solder forms a shiny, cone-shaped fillet. Avoid using too much solder. This can cause short circuits. After that, move to integrated circuits and connectors. Use a soldering iron with a fine tip for precision.
3.Inspection and Testing
After soldering, a visual inspection is crucial. Check for any poor solder joints. Look for bridges between adjacent pins. Also, ensure all components are correctly placed. Then, use a multimeter to test for shorts. Check power and ground connections for resistance. Finally, proceed with a functional test. Apply power to the board cautiously. Observe if it operates as expected. If problems arise, re-check the solder joints. Good assembly ensures long-term reliability.
In conclusion, careful preparation and methodical soldering are key. Always inspect your work thoroughly for a successful project.
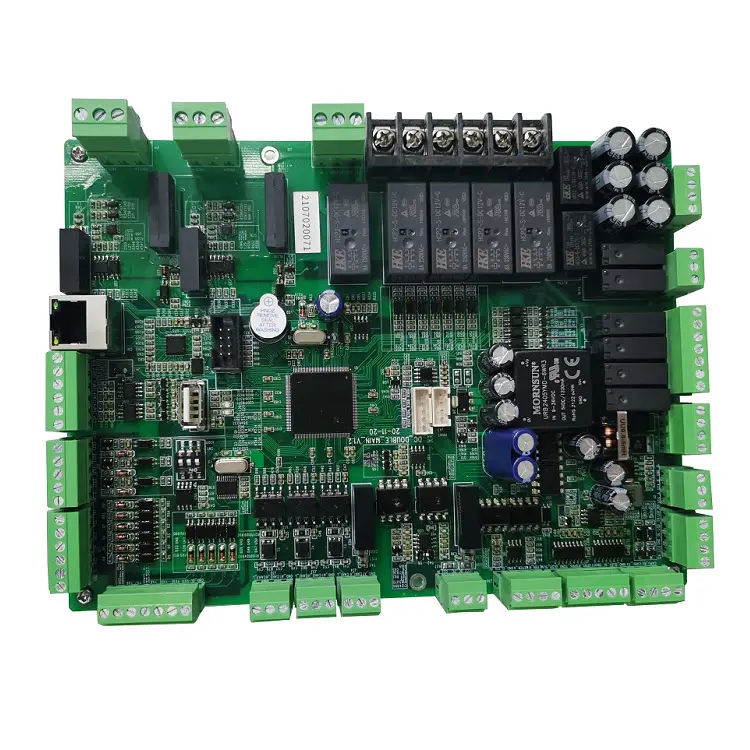
4.Inspection and Testing Phase
Visual inspection is mandatory after soldering. Check for any defective solder joints. Pay attention to bridges between adjacent pins. Simultaneously verify correct component installation. Then use a multimeter to test for shorts. Check power and grounding resistance. Next proceed with functional testing. Apply power to the board cautiously. Observe whether it functions normally. If issues are found, recheck solder joints. Quality assembly ensures long-term stability.
In summary, careful preparation and organized soldering are key. Thorough inspection leads to successful outcomes.
